Data science and the business future of manufacturing and marketing
“The ability to take data — to be able to understand it, to process it, to extract value from it, to visualize it, to communicate it — that’s going to be a hugely important skill in the next decades.” - Hal Varian, chief economist at Google and UC Berkeley professor of information sciences, business, and economics
Data
science continues to evolve as one of the most promising and in-demand
career paths for skilled professionals. Today, successful data
professionals understand that they must advance past the traditional
skills of analyzing large amounts of data, data mining, and programming
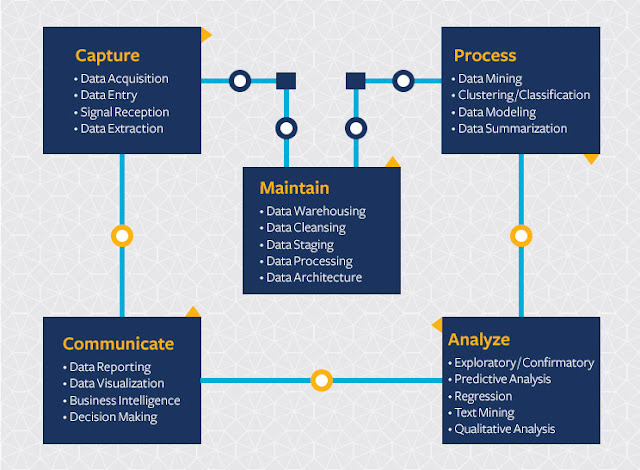
skills. In order to uncover useful intelligence for their organizations,
data scientists must master the full spectrum of the data science life
cycle and possess a level of flexibility and understanding to maximize
returns at each phase of the process.
Effective
data scientists are able to identify relevant questions, collect data
from a multitude of different data sources, organize the information,
translate results into solutions, and communicate their findings in a
way that positively affects business decisions. These skills are
required in almost all industries, causing skilled data scientists to be
increasingly valuable to companies.
Data scientists need to be curious and result-oriented, with exceptional industry-specific knowledge and communication skills that allow them to explain highly technical results to their non-technical counterparts. They possess a strong quantitative background in statistics and linear algebra as well as programming knowledge with focuses in data warehousing, mining, and modeling to build and analyze algorithms.
Glassdoor ranked data scientist as the #1 Best Job in America in 2018 for the third year in a row:
- 28% Demand Increase by 2020
- 4,524 Number of Job Openings
- $120,931 Average Base Salary
- Data Scientist
Data scientists
examine which questions need answering and where to find the related
data. They have business acumen and analytical skills as well as the
ability to mine, clean, and present data. Businesses use data scientists
to source, manage, and analyze large amounts of unstructured data.
Results are then synthesized and communicated to key stakeholders to
drive strategic decision-making in the organization.Skills needed: Programming skills (SAS, R, Python), statistical and mathematical skills, storytelling and data visualization, Hadoop, SQL, machine learning
- Data Analyst
Data analysts
bridge the gap between data scientists and business analysts. They are
provided with the questions that need answering from an organization and
then organize and analyze data to find results that align with
high-level business strategy. Data analysts are responsible for
translating technical analysis to qualitative action items and
effectively communicating their findings to diverse stakeholders.Skills needed: Programming skills (SAS, R, Python), statistical and mathematical skills, data wrangling, data visualization
- Data Engineer
Data engineers manage exponential amounts of rapidly changing data. They focus on the development, deployment, management, and optimization of data pipelines and infrastructure to transform and transfer data to data scientists for querying.
Skills needed: Programming languages (Java, Scala), NoSQL databases (MongoDB, Cassandra DB), frameworks (Apache Hadoop)
- Average salary for different data jobs :
- Data analyst: $65,470
- Data scientist: $120,931
- Senior data scientist: $141,257
- Data engineer: $137,776
- Data analyst: $65,470
- Data scientist: $120,931
- Senior data scientist: $141,257
- Data engineer: $137,776












No comments